Revolutionizing Healthcare: Unleashing the Potential of Stem Cell Therapy


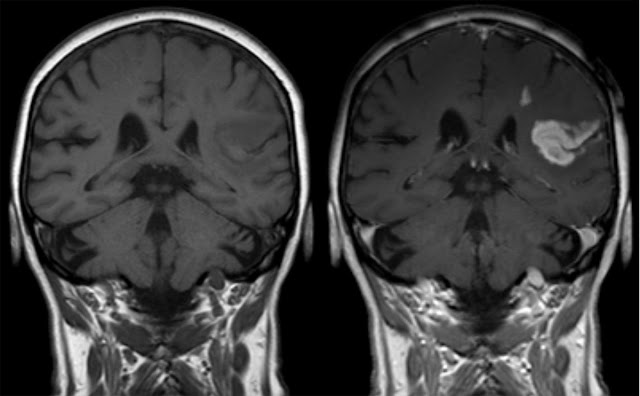 |
| Contrast Media/Contrast Agent |
Contrast media, also known as
contrast agents, play a crucial role in medical imaging procedures. They are
substances used to enhance the visibility of specific tissues, organs, or blood
vessels during diagnostic imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans,
and angiography. By introducing contrast media into the body, healthcare
professionals can obtain clearer and more detailed images, aiding in the
accurate diagnosis and treatment of various medical conditions.
Contrast
media are designed to have different properties than the surrounding
tissues, allowing them to stand out and provide better contrast in the images.
They can be administered orally, intravenously, rectally, or directly into
specific body cavities, depending on the type of procedure and the area being
examined.
There are two main types of
contrast media: iodinated contrast media and gadolinium-based contrast agents
(GBCAs). Iodinated contrast media contain iodine, which is highly radio-opaque
and absorbs X-rays, making them ideal for X-ray and CT scans. These agents are
commonly used to visualize blood vessels, the gastrointestinal tract, and other
structures. Iodinated contrast media can be either high-osmolality or low-osmolality,
depending on their concentration and osmolarity. Low-osmolality agents are
generally preferred as they cause fewer adverse reactions.
On the other hand, GBCAs are used
in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. Gadolinium, a rare earth metal, is
the key component in these agents. GBCAs work by altering the magnetic
properties of nearby water molecules, enhancing the contrast between different
tissues. This allows for detailed visualization of organs, tumors, and blood
vessels in MRI images.
Both iodinated contrast media and
GBCAs have their own benefits and considerations. Iodinated contrast media are
readily available, relatively inexpensive, and can be used in patients with
impaired kidney function. However, they may cause allergic reactions and have a
small risk of kidney damage, particularly in patients with pre-existing renal
conditions. GBCAs, on the other hand, are generally considered safer, with a
lower risk of adverse reactions. However, in rare cases, they have been
associated with a condition called nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF),
primarily affecting patients with severe kidney disease.
It is essential for healthcare
professionals to carefully assess the patient's medical history, allergies, and
renal function before administering contrast media. They should also inform
patients about the potential risks and benefits associated with the procedure.
Contrast media or contrast agents
are essential tools in modern medical imaging. They provide enhanced visibility
of tissues, organs, and blood vessels, enabling healthcare professionals to
make accurate diagnoses and develop appropriate treatment plans. Whether it is
iodinated contrast media for X-rays and CT scans or gadolinium-based contrast
agents for MRI, these substances have revolutionized diagnostic imaging,
improving patient care and outcomes. However, their use requires careful consideration
of the individual patient's condition and the potential risks involved. By
using contrast media judiciously and following best practices, healthcare
providers can harness their benefits while minimizing any associated risks.
Comments
Post a Comment